In this blog we are going to see how can we use Allure-2 Annotations in our test cases.
If you are interested to know about Allure-1 annotations, one of my old blog you may read.
What is Alure?
Allure is an opensource report engine built using AngularJS. It generates report based on maven surefire plugins. It has support for junit, testNG, cucumber-java, selenide, pytest, behav, jasmine, Mocha, RSpec, Spock, PHPUnit , SpecFlow, NUnit, MSTest etc unit testing framework. It has command line interface to generate report . And it has supports for popular CI/CD platform like jenkins, TeamCity, Banboo, Gradle, Maven, CodeFresh.
I am not putting details on why we need allure, to know details about allure reporting format, please see my old post
Example With Junit5
- POM.XML structure
- Example Test cases
- Application to test
Key Points in POM
- Surefire Plugins configuration
- Reporting Configuration
- Supported Maven Site Plugins configurations
- Allure Dependency for using allure annotation in Code.
- Allure depends on aspectj, log4j, please check those.
Allure Properties
Allure reports comes with predefine properties. Here are the default values
allure.results.directory=target/allure-results
allure.link.issue.pattern=https://example.org/browse/{}
allure.link.tms.pattern=https://example.org/browse/{}
So, what are the annotations for Allure 2 that we can use. Here are the list. I am describing one by one.
Commands to see report
- To run test
mvnw -Dtest.suite=org.automation.junit5.suites.AllureExamples.class clean test - To generate & view report locally
mvnw site io.qameta.allure:allure-maven:report io.qameta.allure:allure-maven:serve
For quick run, I have added two files for windows allure-example.bat and build-show-report.bat linux based OS allure-example.sh and build-show-report.sh. Just run them one by one.
The Application Under Test
In the whole example, I am using this simple calculator class to test.
package org.automation;
import io.qameta.allure.Attachment;
import io.qameta.allure.Step;
public class Calculator {
@Step
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
@Step
public int mod(int a, int b) {
return a % b;
}
@Step
public int div(int a, int b) {
return a % b;
}
@Step
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
@Step
public int add(int[] a) {
int result = 0;
for (int i : a) {
result += i;
}
return result;
}
@Step("adding Integers with {} ")
public Integer add(Integer... numbers) {
Integer result = new Integer(0);
for (Integer i : numbers) {
result += i;
}
return result;
}
@Step
public <T extends Number> T add(T... t) {
Double sum = new Double(0.0);
for (T i : t) {
sum += i.doubleValue();
}
return (T) sum;
}
@Step
@Attachment
public String add(String... strings){
if(null==strings || strings.length<=0)
{
return "empty_input";
}
else
{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (String a:strings){
sb.append(a);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
}
@Step :
Each step method to perform a test. That means, when you write your test, your test might need multiple methods to call. Annotate to each method which are used in a @Test.
Scope Of Use : Methods. Can be used with methods only
Parameters : It can take String value which can be description of the step.
Example :
I have included steps in all methods of calculator class. That means every time any calculator method is called for testing, it will be shown in Allure report as step.
- This shows default behavior of @Step. That means , method name will be used as step description.
@Step
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
In Report :
- This shows custom step sentence with parameters which is indicated by
{}
@Step("adding Integers with {} ")
public Integer add(Integer... numbers) {
Integer result = new Integer(0);
for (Integer i : numbers) {
result += i;
}
return result;
}
In Report :
@AllureId : For Allure Enterprise Solution
Scope Of Use : Methods Parameters : It can take String
Example :
I am not using Allure corporate service, no I dont have any example for this. This is mainly Used by Allure Enterprise to link test cases with related test methods.
@Attachment :
Usually when a method returns a String or Byte array, we can attach this to allure report. That means, if we take any screenshot taking method, we can easily use @Attachment to include into report.
Scope Of Use : Methods
Parameters : Attachment Name, Attachment type, attached file extension. All are string
Example :
in the example, I am including @Attachment in method call and utility where I am taking screenshot.
a. This will get the return of the method and save as attachement
@Step
@Attachment
public String add(String... strings){
if(null==strings || strings.length<=0)
{
return "empty_input";
}
else
{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (String a:strings){
sb.append(a);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
In the report we can see like this
b. This will attach where screenshot was called. I have added a name just to show we can set name of the attachment.
@Attachment(value = "imageCaptured")
public static byte[] capturePNG() throws IOException, AWTException {
byte[] out = null;
BufferedImage screencapture = new Robot().createScreenCapture(
new Rectangle(Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize()));
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(screencapture, "png", bo);
out = bo.toByteArray();
bo.close();
return out;
}
In the report we can see like this
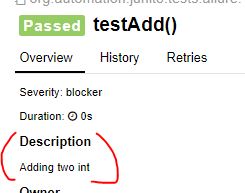
@Description :
When you want to add mode details to your test , use this as description of a test. Usually I prefer to put manual testcase title as description so that in report we can see.
Scope Of Use : Methods
Parameters : Description string & boolean if we want to extract description from method’s JavaDoc
Example :
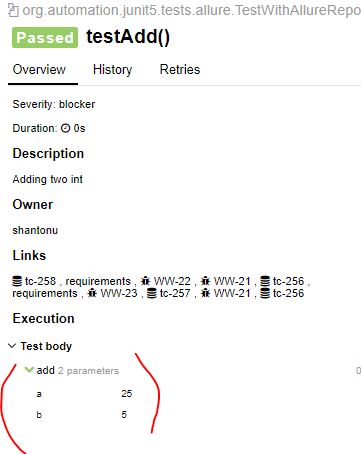
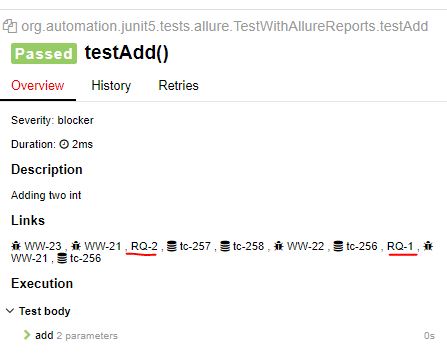
@Test
@Description("Adding two int ")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
In Report :
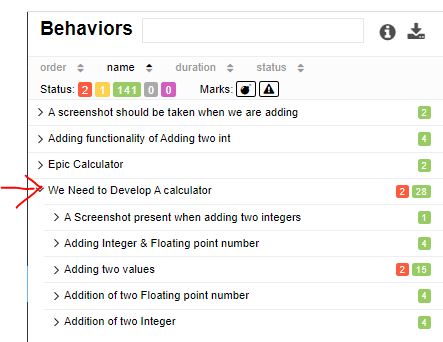
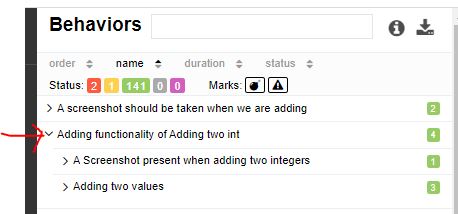
@Epic :
An Epic is set of work which can be divided in smaller stories. Basic Idea about EPIC can be found here
In summary, A large feature or theme that can span several releases is called EPIC
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes
Parameters : Description string.
Example :
In class
@Epic("We Need to Develop A calculator")
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
In Report :
In method
@Test
@Epic("Adding functionality of Adding two int ")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
In Report :
Note : there are two method which has same epic name, so, two test will be under this single epic
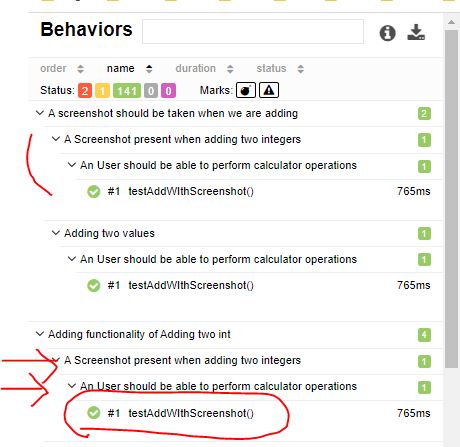
@Epics :
This is for supporting multiple EPICs together in a single test.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes
Parameters : Array of EPIC
Example :
In method
@Test
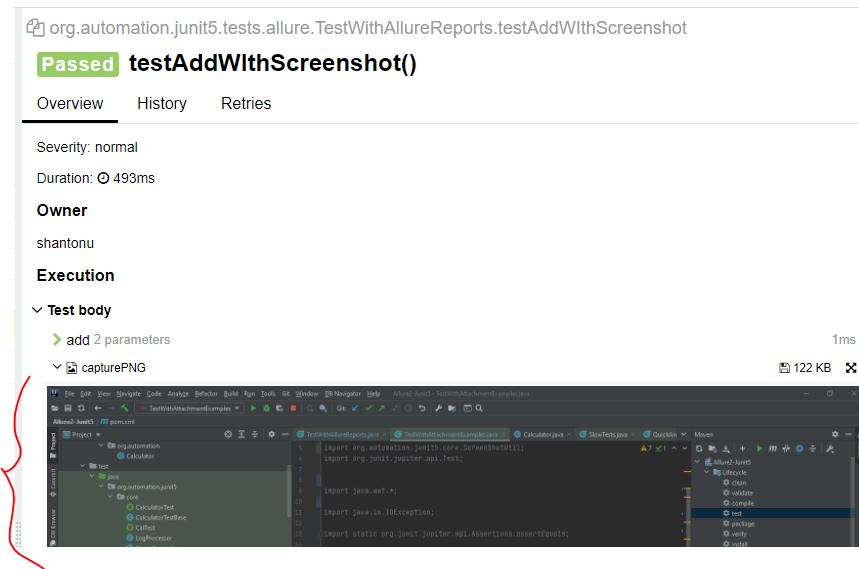
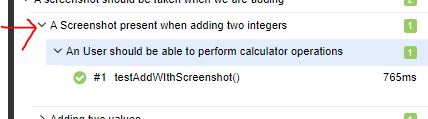
@Epics(@Epic("Adding functionality of Adding two int "),@Epic("A screenshot should be taken when we are adding"))
public void testAddWIthScreenshot() throws IOException, AWTException {
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
ScreenShotUtil.capturePNG();
}
In Report :
Note : In here you can see testAddWIthScreenshot() present under both epic
@Feature :
A functionality that we deliver in a version of a release. It may contain multiple stories but make sure they are released in single version.
It is similar to EPIC but scope is single version.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes
Parameters : Description string.
Example :
In class
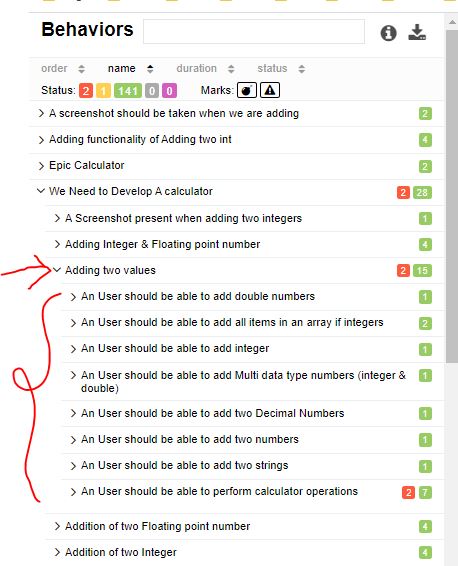
@Feature("Adding two values")
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
In Report :
In method
@Test
@Feature("A Screenshot present when adding two integers")
public void testAddWIthScreenshot() throws IOException, AWTException {
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
ScreenShotUtil.capturePNG();
}
In Report :
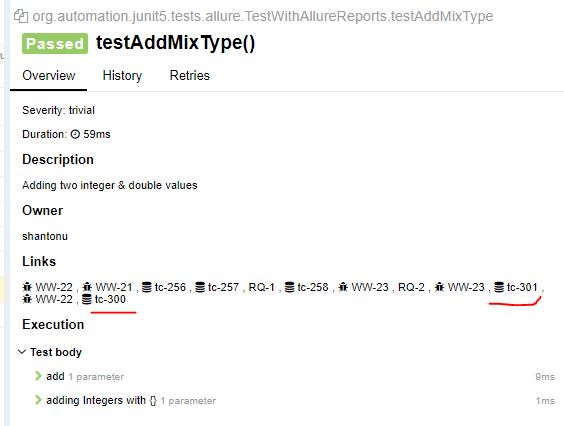
@Features :
This is same as @Feature but with multiple entry. That means, this allows multiple Feature descriptions attached with a test class/method
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : Array of feature
Example :
In method
@Test
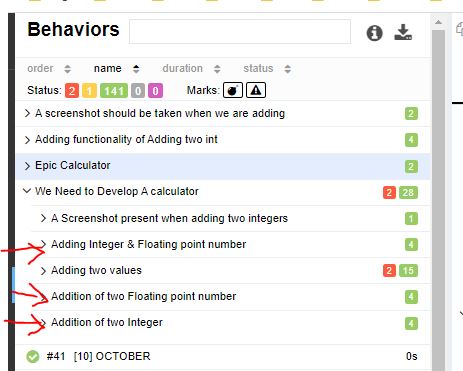
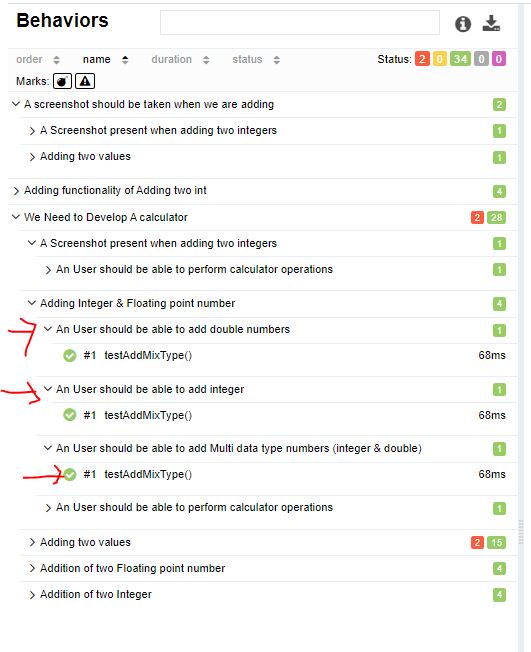
@Features({@Feature("Addition of two Integer"),
@Feature("Addition of two Floating point number"),
@Feature("Adding Integer & Floating point number")})
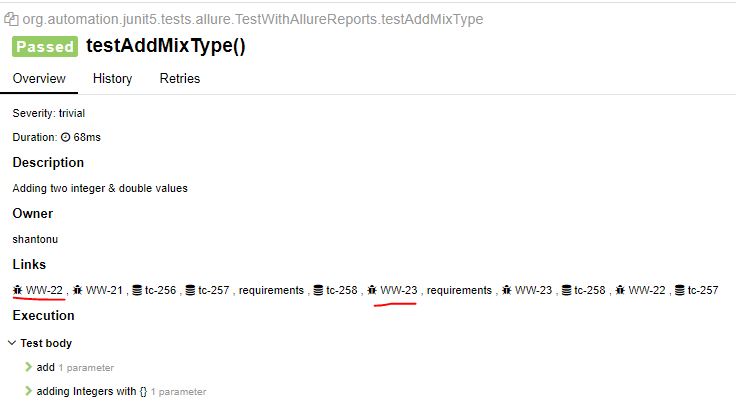
public void testAddMixType(){
Double[] data_double = new Double[]{15.0,25.1,4.9};
Integer[] data_int = new Integer[]{15,5,10};
assertEquals(45.0,myCal.add(data_double));
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(data_int));
}
In Report :
@Story :
A short (the smallest possible) requirement written in end user perspective. A good read is here
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : It can take String value which can be description of the step.
Example :
In class
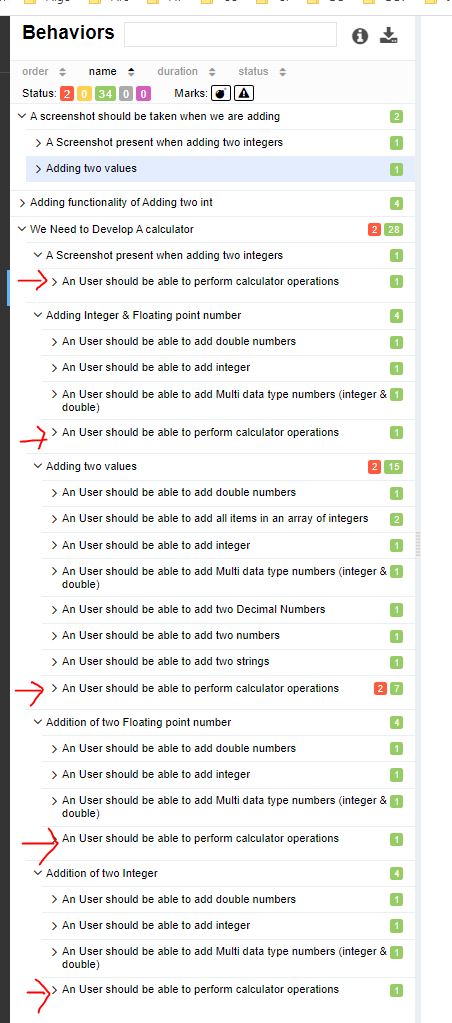
@Story("An User should be able to perform calculator operations ")
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
In Report :
Note : As story is the lowest part of epic-feature-story hierarchy. As we have put this line as story of a class, you will see this story added to all methods inside that class.
In Method :
@Test
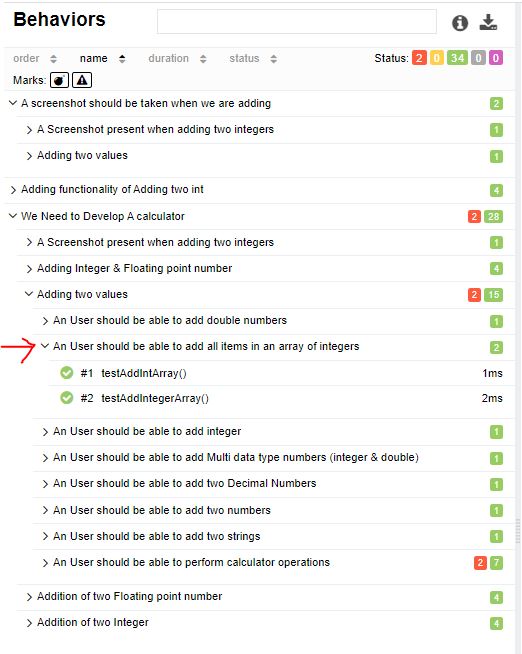
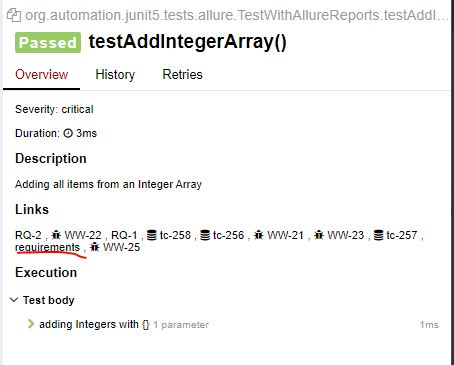
@Story("An User should be able to add all items in an array of integers")
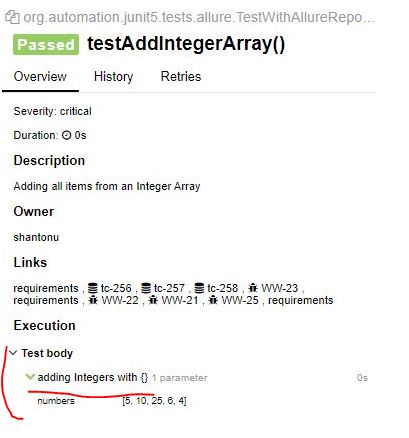
public void testAddIntegerArray(){
Integer[] data = new Integer[]{5,10,25,6,4};
assertEquals(50,myCal.add(data));
}
In Report :
@Stories :
This is same as @Story but with multiple entry. That means, this allows multiple Story descriptions attached with a test class/method
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : Array of Story
Example :
In a method
@Test
@Stories({
@Story("An User should be able to add Multi data type numbers (integer & double)"),
@Story("An User should be able to add integer"),
@Story("An User should be able to add double numbers")})
public void testAddMixType(){
Double[] data_double = new Double[]{15.0,25.1,4.9};
Integer[] data_int = new Integer[]{15,5,10};
assertEquals(45.0,myCal.add(data_double));
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(data_int));
}
In Report :
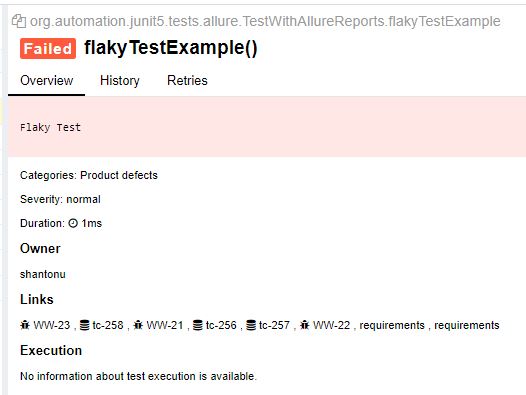
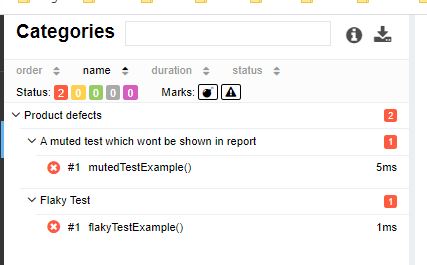
@Flaky :
Used with unstable tests. In allure report we can see annotated test as unstable.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : None
Example :
I am making a test to fail intentionally.
- In method
@Test
@Flaky
public void flakyTestExample(){
Assertions.fail("Flaky Test");
}
In Report :
It has the text which i have added in assertion fail.
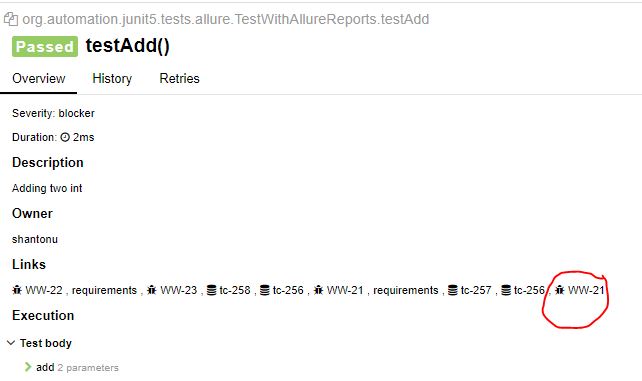
@Issue :
Linking a rest with issues.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : String to link issue tracker’s original issue link
Example :
In Method :
@Test
@Issue("WW-21")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
In Report :
@Issues :
This is same as @Issue but with multiple entry. That means, this allows multiple Issue link attached with a test class/method
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : Arrays of Issue
Example :
In method :
@Test
@Issues({@Issue("WW-22"),@Issue("WW-23")})
public void testAddMixType(){
Double[] data_double = new Double[]{15.0,25.1,4.9};
Integer[] data_int = new Integer[]{15,5,10};
assertEquals(45.0,myCal.add(data_double));
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(data_int));
}
In Report :
In Class :
@Issues({@Issue("WW-22"),@Issue("WW-21"),@Issue("WW-23")})
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
In Report :
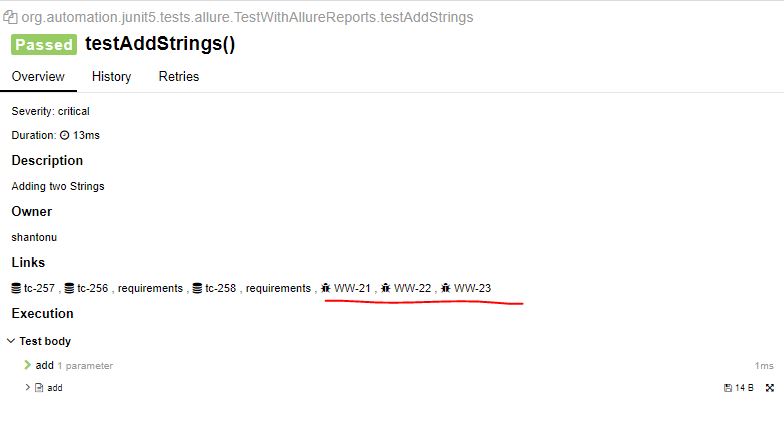
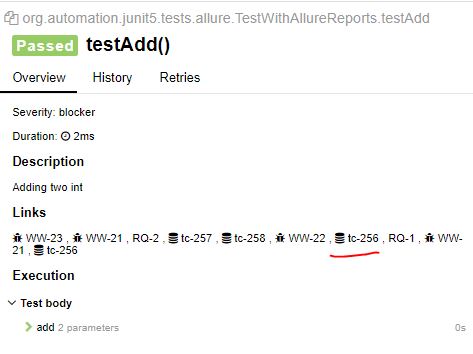
Note : As I have attached "WW-22,WW-21,WW-23 in the class, all of the test method will get this number by default.
@Lead :
This annotation can be used to define a test case LEAD information.
Scope Of Use : Methods
Parameters : String value as name of the lead person
Example :
@Test
@Lead("shantonu.sarker")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
Note : @Lead information will not be shown in report. In result JSON, you can see.
@Link :
We can link any URL with @Link. It can be any external link /reference.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : It takes
- name , a string to represent link text
- url , a string to represent an actual link
- type , a string to represent what type of link
- value , similar to name
Example :
In Method :
@Test
@Link(name = "requirements", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/add-numbers",type = "Trello")
public void testAddIntegerArray(){
Integer[] data = new Integer[]{5,10,25,6,4};
assertEquals(50,myCal.add(data));
}
In Report :
@Links :
This is same as @Link but with multiple entry. That means, this allows multiple Links attached with a test class/method
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : Arrays of Links
Example :
In Class :
@Links({ @Link(name = "RQ-1", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/add-numbers",type = "Trello"),
@Link(name = "RQ-2", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/product-numbers",type = "Trello")})
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
In Report :
Note : As RQ-1, RQ-2 added in class level, all test cases will have those two links.
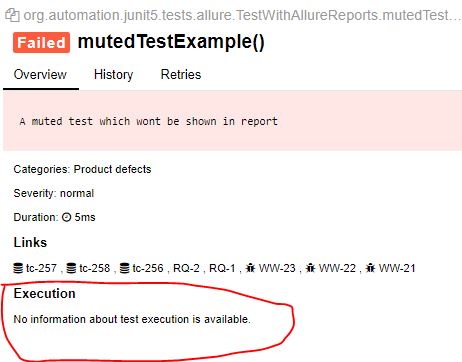
@Muted :
If you want to exclude any test from Allure report, use @Muted.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters :None
Example :
In Method :
@Test
@Muted
public void mutedTestExample(){
Assertions.fail(" A muted test which wont be shown in report");
}
And we cant see this in report.
In Report :
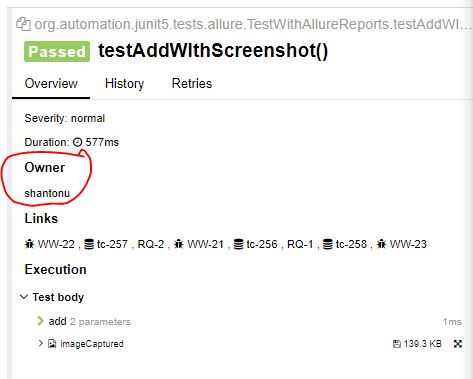
@Owner :
This allows to put owner information of a test case presentable Allure report.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters :Takes string as name of owner
Example :
in method :
@Test
@Owner("shantonu")
public void testAddWIthScreenshot() throws IOException, AWTException {
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
ScreenShotUtil.capturePNG();
}
In Report :
In Class :
@Owner("shantonu")
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {...}
Note : If you add owner info in class level, all of your test methods will get the owner info.
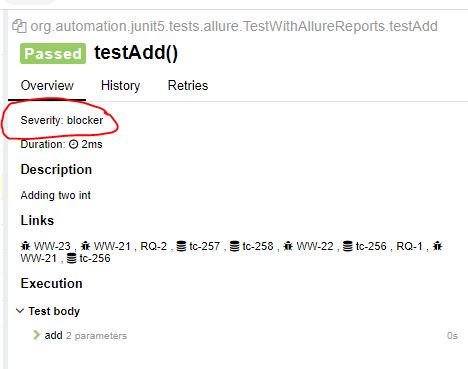
@Severity :
We can prioritize out test by putting Severity information in Allure report using @Severity. Allure has builtin constants to use it with.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters :Takes SeverityLevel values. Allure 2.0 has following Severities (enum name io.qameta.allure.SeverityLevel)
- BLOCKER(“blocker”),
- CRITICAL(“critical”),
- NORMAL(“normal”),
- MINOR(“minor”),
- TRIVIAL(“trivial”);
Example :
In Class :
@Severity(SeverityLevel.NORMAL)
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {
In Method :
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.BLOCKER)
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
In Report :
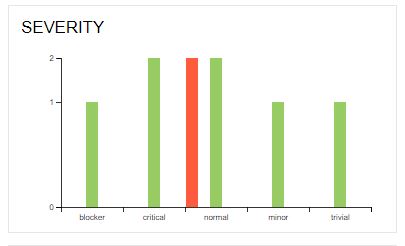
Note : if you use this in class level, all test methods will have that value by default. Any test method value will override class level declearation.
- In Graph view, you can see this
@TmsLink : Test Management System Links
We can add test management tracker/system links with test cases. This will provide complete link in report. URL prefix can be configured using allure.link.tms.pattern property.
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : It can take String value which is the link of management system.
For example, if our test case on TMS link is https://tms.mycompany.com/browse/tc-256, then we can use tc-256 as value here.
Example :
In method :
@Test
@TmsLink("tc-256")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
In Report :
- Link in allure.properties :
allure.link.tms.pattern=https://example.org/browse/{}where our provided text will put in{}section.
@TmsLinks :
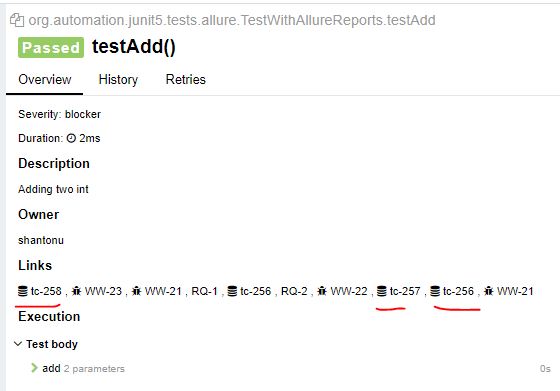
This is same as @TmsLink but with multiple entry. That means, this allows multiple TMS link attached with a test class/method
Scope Of Use : Methods & Classes.
Parameters : It can take String value which can be description of the step.
Example :
In Class :
@TmsLinks({@TmsLink("tc-257"), @TmsLink("tc-258"), @TmsLink("tc-256")})
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {..}
In Report :
In Method :
@Test
@TmsLinks({@TmsLink("tc-300"), @TmsLink("tc-301")})
public void testAddMixType(){
Double[] data_double = new Double[]{15.0,25.1,4.9};
Integer[] data_int = new Integer[]{15,5,10};
assertEquals(45.0,myCal.add(data_double));
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(data_int));
}
In Report :
Note : If we add this in class level, all test methods will get the links.
The test code
Finally, I have two part of the test code. I put CalculatorTestBase.java as base test case and actual test case will be TestWithAllureReports.java.Here are the source code
Test Base
package org.automation.junit5.core;
import io.qameta.allure.listener.StepLifecycleListener;
import io.qameta.allure.model.StepResult;
import org.automation.Calculator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class CalculatorTestBase implements StepLifecycleListener {
protected Calculator myCal;
public Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@BeforeAll
public static void initForAllTest(){
}
@AfterAll
public static void cleanupForAllTest(){
}
@BeforeEach
public void initTest()
{
myCal = new Calculator();
}
@Override
public void beforeStepStop(StepResult result) {
logger.info("Finished step : {}",result.getName());
}
}
Test Case
package org.automation.junit5.tests.allure;
import io.qameta.allure.*;
import org.automation.junit5.core.CalculatorTestBase;
import org.automation.junit5.core.ScreenShotUtil;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
/**
* Created by shantonu on 3/29/2021
*/
@Epic("We Need to Develop A calculator")
@Feature("Adding two values")
@Story("An User should be able to perform calculator operations ")
@Owner("shantonu")
@Issues({@Issue("WW-22"),@Issue("WW-21"),@Issue("WW-23")})
@Links({ @Link(name = "RQ-1", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/add-numbers",type = "Trello"),
@Link(name = "RQ-2", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/product-numbers",type = "Trello")})
@Severity(SeverityLevel.NORMAL)
@TmsLinks({@TmsLink("tc-257"), @TmsLink("tc-258"), @TmsLink("tc-256")})
public class TestWithAllureReports extends CalculatorTestBase {
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.BLOCKER)
@Description("Adding two int ")
@Lead("shantonu.sarker")
@Story("An User should be able to add two numbers")
@Issue("WW-21")
@Epic("Adding functionality of Adding two int ")
@TmsLink("tc-256")
public void testAdd(){
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
}
@Test
@Epics({@Epic("Adding functionality of Adding two int "),@Epic("A screenshot should be taken when we are adding")})
@Feature("A Screenshot present when adding two integers")
@Owner("shantonu")
public void testAddWIthScreenshot() throws IOException, AWTException {
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(25,5));
ScreenShotUtil.capturePNG();
}
@Test
@Description("Adding two Strings ")
@Story("An User should be able to add two strings")
@Severity(SeverityLevel.CRITICAL)
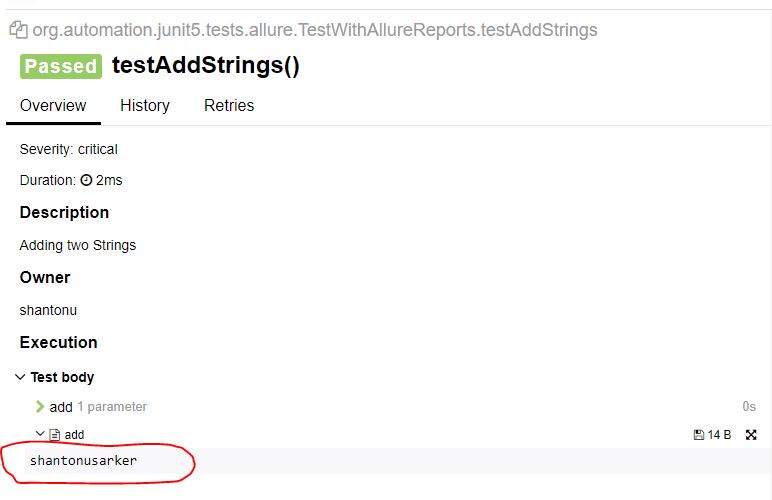
public void testAddStrings(){
assertEquals("shantonusarker",myCal.add("shantonu","sarker"));
}
@Test
@Muted
public void mutedTestExample(){
Assertions.fail(" A muted test which wont be shown in report");
}
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.MINOR)
@Description("Adding all items from an int Array")
@Story("An User should be able to add all items in an array of integers")
public void testAddIntArray(){
int[] data = {5,10,25,6,4};
assertEquals(50,myCal.add(data));
}
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.CRITICAL)
@Description("Adding all items from an Integer Array")
@Story("An User should be able to add all items in an array of integers")
@Issue("WW-25")
@Link(name = "requirements", url="https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/examples/add-numbers",type = "Trello")
public void testAddIntegerArray(){
Integer[] data = new Integer[]{5,10,25,6,4};
assertEquals(50,myCal.add(data));
}
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.TRIVIAL)
@Description("Adding two integer & double values")
@Stories({@Story("An User should be able to add Multi data type numbers (integer & double)"),
@Story("An User should be able to add integer"),
@Story("An User should be able to add double numbers")})
@Features({@Feature("Addition of two Integer"),
@Feature("Addition of two Floating point number"),
@Feature("Adding Integer & Floating point number")})
@Issues({@Issue("WW-22"),@Issue("WW-23")})
@TmsLinks({@TmsLink("tc-300"), @TmsLink("tc-301")})
public void testAddMixType(){
Double[] data_double = new Double[]{15.0,25.1,4.9};
Integer[] data_int = new Integer[]{15,5,10};
assertEquals(45.0,myCal.add(data_double));
assertEquals(30,myCal.add(data_int));
}
@Test
@Severity(SeverityLevel.NORMAL)
@Description("Adding two decimal values")
@Flaky
@Story("An User should be able to add two Decimal Numbers")
public void testAddDecimal(){
double a = 2.4, b =5.2;
assertEquals(7.6, myCal.add(a,b), "double adding ");
}
@Test
@Flaky
public void flakyTestExample(){
Assertions.fail("Flaky Test");
}
}
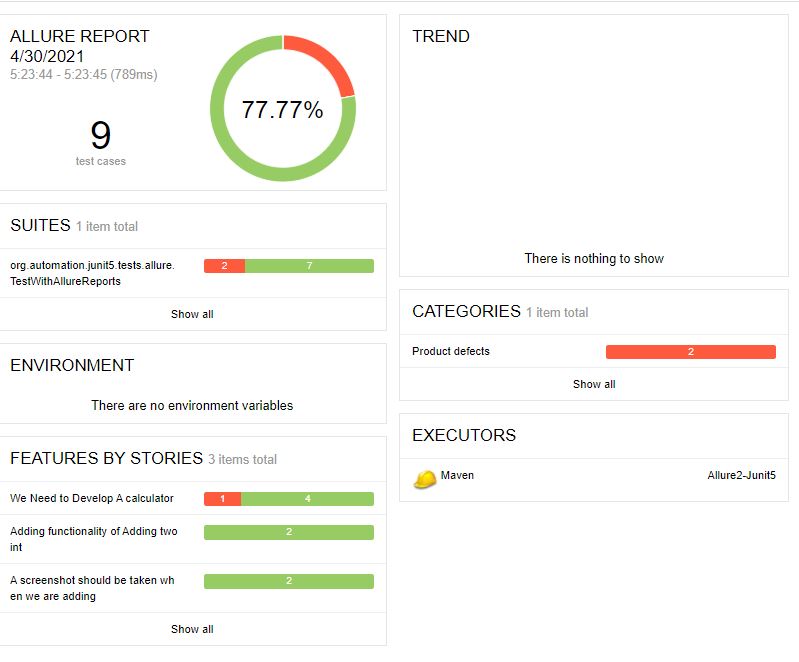
Allure Report
- Overall
- Failed & invalid tests