In this article we are going to see how we can use Vim.
What is VIM?
Vim is the most popular cli editor used mostly in linux/unix like Os. System admins, developer use vim daily basis for scripting and coding. You can see popularity of VIM in stackoverflow only for exiting VIM.
installation via apt
- Vim CLI only
sudo apt install vim - Vim Gtk3 GUI
sudo apt install vim-gtk3 - Vim tiny version
sudo apt install vim-tiny - neovim
sudo apt install neovim - Vim athena GUI
sudo apt install vim-athena - Vim Gtk GUI
sudo apt install vim-gtk - Another Vim tiny version
sudo apt install vim-nox
How it works?
Vim has multiple modes :
- Normal Mode : For navigation . When you press ESC, all modes come back to this mode.
- Insert Mode : For insert/edit. Pressing
iwill go in this mode. - View/visual Mode : For navigation and manipulation of text selections
- Command mode : For inserting editor command. Press
ESCfor command mode - Select Mode : Similar to visual mode but more functionality.
- Ex-mode : Similar to the command-line mode but optimized for batch processing.
How VIM runs command
This will show how vi actually runs the command. This will help you to understand how VIM works with exit command example.
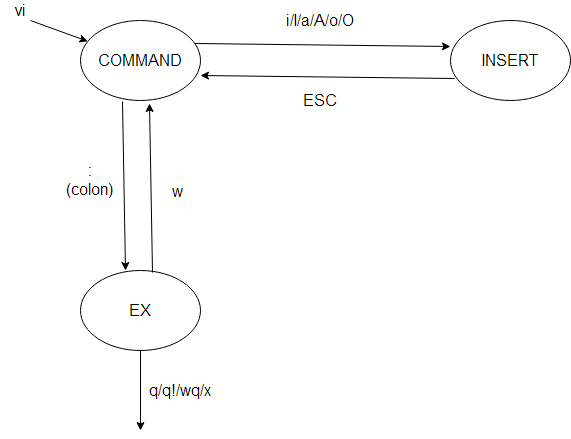
Command Mode Basics
- To exit :
:q - To save and exit
:wq - To quit without saving
:q! - to write and quit even if file has only read permission
:wq! - to write and quit
:xor:exit - to quit all
:qa - to quit without saving and make Vim return non-zero error
:cq - To delete the unwanted character
x - To undo the last the command and U to undo the whole line
u - To redo
CTRL-R - To append text at the end
A - Move the cursor to the beginning of the word to delete that word
dw - To move the cursor two words forward
2w - To move the cursor to the end of the third word forward
3e - To move to the start of the line
0 - To delete multiple words, we can use dXw, here X can be any number. For 2 words
d2w, for 3 wordsd3w - To delete multiple lines, we can use Xdd . Single line delete
dd, 2 line delete2dd - puts the previously deleted text after the cursor
p - to replace the letter use r+the letter e.g press
rkto replace the letter with k - deletes the word and places you in Insert mode
ce - to change until the end of a word , use ce. example - place the cursor on the u in kuaw it will delete uaw
- to move you to the bottom of the file
G - to move you to the start of the file
gg. Type the number of the line you were on and then G ,like5G - to find a matching ),], or } use
% - to substitute ‘new’ for ‘old’ where g is globally use
:s/old/new/g /backward search n to find the next occurrence and N to search in opposite direction- forward search
? - to run the shell commands
:!, like :!dir, :!ls - TEST Save the file
:w - starts visual mode
vfor selecting - Filename will insert the content into the current file
:r - to replace more than one character
R - opens a line below the cursor and start Insert mode
o - opens a line above the cursor
O - inserts text after the cursor
a - inserts text after the end of the line
A - moves to the end of a word
e - copy/yanks one word
yw - operator yanks/copies text
y - puts (pastes)
p - Enters Replace mode until
is pressed , use ```R ``` - to jump from one window to another
ctrl-w - to know suggested command type first letter of a command and press
ctrl+D. For example, if you type :e andctrl+D, you should see this
- Format to change command , Syntax operator _number_ motion . where
- operator - is what to do, such as d for delete
- number - is an optional count to repeat the motion
- motion - moves over the text to operate on, such as w (word), $ (to the end of line), etc.