In this article we are going to learn about Interpreter Design Pattern.
- What is Interpreter design pattern?
- What are the basic principles?
- How to implement
- where we can use this.
I have used Java with Eclipse and C# with VS2010.
What is Interpreter Design Pattern?
Interpreter pattern is used to convert one represent of data into another representation of data.
That means , if we have a set of data that need conversion before output, we can use the pattern.
Let’s say, water unit converter. If we want to convert our input value from liter/gallons/quartz/pints/cups/tablespoon to liter/gallons/quartz/pints/cups/tablespoon then we should have bunch of functions to converting each other. In this case , we will have 30 functions to convert unit to each other. And we need a lot of conditions to check which will be kind of messy. But, if we apply Interpreter, then we can easily apply the conversion.
Or, if we want to convert a predefine Text/CSV context file to let say html/xml/xaml/json file. We can also apply this pattern to keep it simple and manageable.
Or, think of db quarry to SQL statement conversion. It is very useful for this interpretation.
Interpreter patter have basic 3 elements.
- Context : which will be interpreted
- Expression that instructs the interpretation. Think of an abstract class defines all the methods needed to perform different conversions.
- Terminal (the expression implemented) that provides specific conversions of context-ed data.
Principles :
- Get inputs for conversion(interpretation)
- Map to predefined output.
- Serve client with abstraction of interpretation.
UML:
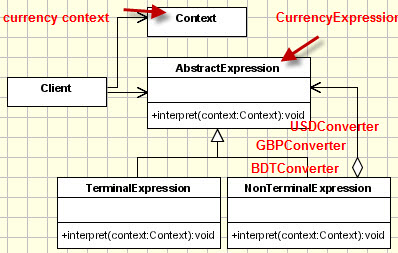
How to Implement?
Before implementing , lets thinks , what it is.
Simply, it will translate. So, we will need a class(out type) to convert which will be context.
And, having a conversational formula inside of a class or abstract class where extended classes will have implemented the conversion functions.
And, a client who will call the context with expressions (may be along with conditions).
Example:
Let’s make a currency converter. We will convert from one currency to another.
For making small example, let consider 4 type of currency USD(USA currency), GBP(UK currency), BDT(Bangladesh currency), MYR(Malaysia currency).
And we need to convert one to another currency conversion.
So , out context is currency conversion.
So, we will have a class representing the context.
I have named as CurrencyContext that contains getter & setters only with values.
public class CurrencyContext {
private int input;
private double output;
public int getInput() {
return input;
}
public void setInput(int input) {
this.input = input;
}
public double getOutput() {
return output;
}
public void setOutput(double output) {
this.output = output;
}
public CurrencyContext(int in){
this.input=in;
}
}
And, a currency expression that contains interpretation function along with different type of interpretation methods.
The formulas will be implemented in derived classes.
public abstract class CurrencyExpression {
public abstract double usd(int input);
public abstract double gbp(int input);
public abstract double bdt(int input);
public abstract double myr(int input);
public void interpret(CurrencyContext acontext, String type){
if(type=="usd"){
acontext.setOutput(usd(acontext.getInput()));
}else if(type=="bdt"){
acontext.setOutput(bdt(acontext.getInput()));
}else if(type=="gbp"){
acontext.setOutput(gbp(acontext.getInput()));
}else if(type=="myr"){
acontext.setOutput(myr(acontext.getInput()));
}
}
}
And, extending real expressions are GBPConverter, MYRConverter, USDConverter, BDTConverter
public class GBPConverter extends CurrencyExpression{
public double usd(int input) {
return input*1.6703;
}
public double gbp(int input) {
return input;
}
public double bdt(int input) {
return input*129.4726;
}
public double myr(int input) {
return input*5.5160;
}
}
public class MYRConverter extends CurrencyExpression{
public double usd(int input) {
return input*0.3028;
}
public double gbp(int input) {
return input*0.1813;
}
public double bdt(int input) {
return input*23.4720;
}
public double myr(int input) {
return input;
}
}
public class USDConverter extends CurrencyExpression{
public double usd(int input) {
return input;
}
public double gbp(int input) {
return input*0.5987;
}
public double bdt(int input) {
return input*77.5164;
}
public double myr(int input) {
return input*3.3025;
}
}
public class BDTConverter extends CurrencyExpression{
public double usd(int input) {
return input*0.0129;
}
public double gbp(int input) {
return input*0.0077;
}
public double bdt(int input) {
return input;
}
public double myr(int input) {
return input*0.0426;
}
}
And, now , lets call them from client who contains main class
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("We will convert BDT 1000 to other languages");
CurrencyContext bdtCurrency = new CurrencyContext(1000);
CurrencyExpression bdConvert = new BDTConverter();
bdConvert.interpret(bdtCurrency, "usd");
System.out.println("After conversion "+bdtCurrency.getOutput());
}
}
Java Example:
- We can also take input of conversion type or even reflection. But, I use simple input parameter to keep the example simple to understand.
- We can also isolate the formula coming from service in background.
- I took exchange rates from XE, so it might be changed.
C# Example :
- I have convert access method as property
- naming and function calling are change due to dot net implementation.
Usages :
- When we need to provide different type of output than system generated default output. Like as reporting.
- When we want to translate a certain data to another format.
- Applying different type of conversions.
- Intermediate formal communication data conversion(one module to talk to another, when new module need a converted data of old module).
- Some time, it can be useful in the maintenance of legacy system data interpretation.