In this article we are going to see how we can use iperf3.
What is iperf3?
Iperf is a network speed test utilities. It is more accurate than speedtest-cli and you can define your server to test with.
- Default iperf3 server listens on TCP port 5201
- Iperf has client mode & server mode
- Client mode create request to test with server.
- Server mode runs in background to receive request for speed test.
Why iperf3?
- Network speed test in cli
- Intranet speed test
- Testing speed among different type of network in same organization or in different part of the world.
Installation
-
Install via APT
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y iperf3 -
Manually install, download from here
Run iperf3 server
iperf3 -s
Run iperf3 server in Background
iperf3 -s D
Run iperf3 client to test
iperf3 -c ip_or_address_of_server
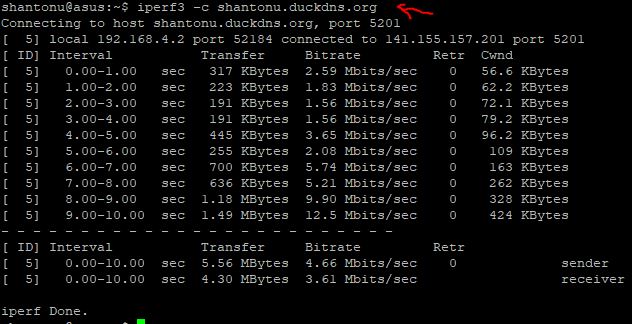
Iperf3 Testing Example
iperf3 -c shantonu.duckdns.org
Create iperf3 service in linux
Create a file iperf3.service at /etc/systemd/system/ or $HOME/.config/systemd/user/iperf3.service location
# /etc/systemd/system/iperf3.service
# User service: $HOME/.config/systemd/user/iperf3.service
[Unit]
Description=iperf3 server
After=syslog.target network.target auditd.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/iperf3 -s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
And run the service :
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable iperf3.service
sudo systemctl start iperf3
sudo systemctl status iperf3
if you want log for this service (optional) :
sudo journalctl -f -u iperf3
More Options
There are more CLI options, here is the whole list.
Usage: iperf [-s|-c host] [options]
iperf [-h|--help] [-v|--version]
Server or Client:
-p, --port # server port to listen on/connect to
-f, --format [kmgKMG] format to report: Kbits, Mbits, KBytes, MBytes
-i, --interval # seconds between periodic bandwidth reports
-F, --file name xmit/recv the specified file
-A, --affinity n/n,m set CPU affinity
-B, --bind <host> bind to a specific interface
-V, --verbose more detailed output
-J, --json output in JSON format
--logfile f send output to a log file
-d, --debug emit debugging output
-v, --version show version information and quit
-h, --help show this message and quit
Server specific:
-s, --server run in server mode
-D, --daemon run the server as a daemon
-I, --pidfile file write PID file
-1, --one-off handle one client connection then exit
Client specific:
-c, --client <host> run in client mode, connecting to <host>
-u, --udp use UDP rather than TCP
-b, --bandwidth #[KMG][/#] target bandwidth in bits/sec (0 for unlimited)
(default 1 Mbit/sec for UDP, unlimited for TCP)
(optional slash and packet count for burst mode)
-t, --time # time in seconds to transmit for (default 10 secs)
-n, --bytes #[KMG] number of bytes to transmit (instead of -t)
-k, --blockcount #[KMG] number of blocks (packets) to transmit (instead of -t or -n)
-l, --len #[KMG] length of buffer to read or write
(default 128 KB for TCP, 8 KB for UDP)
--cport <port> bind to a specific client port (TCP and UDP, default: ephemeral port)
-P, --parallel # number of parallel client streams to run
-R, --reverse run in reverse mode (server sends, client receives)
-w, --window #[KMG] set window size / socket buffer size
-C, --congestion <algo> set TCP congestion control algorithm (Linux and FreeBSD only)
-M, --set-mss # set TCP/SCTP maximum segment size (MTU - 40 bytes)
-N, --no-delay set TCP/SCTP no delay, disabling Nagle's Algorithm
-4, --version4 only use IPv4
-6, --version6 only use IPv6
-S, --tos N set the IP 'type of service'
-L, --flowlabel N set the IPv6 flow label (only supported on Linux)
-Z, --zerocopy use a 'zero copy' method of sending data
-O, --omit N omit the first n seconds
-T, --title str prefix every output line with this string
--get-server-output get results from server
--udp-counters-64bit use 64-bit counters in UDP test packets
--no-fq-socket-pacing disable fair-queuing based socket pacing
(Linux only)