In this article we are going to learn about Prototype Design Pattern.
- What is Prototype design pattern?
- What are the basic principles?
- How to implement
- where we can use this.
I have used Java with Eclipse and C# with VS2010.
What is Prototype Design Pattern?
Prototype patter allows us to create customized objects without knowing their class or any details of how to create them.
It uses cloning behavior to create new objects that improves performance.
Prototype allows run time adding any subclass instance of a known super class.
Let’s consider a puzzle game. Where we need similar type of building blocks. That time we can clone the object to save the memory for new object creation.
Or, in a database testing domain, we need to clone the data containing object to get exact scenario for validation.
Or ever think of a animal planet(most common example ) where we need dog, cat or any type of animal cloned while execution. It will let use creating new dog or cat but we can clone existing(previously created) object to clone and use.
Prototype is similar to factory pattern but practically in prototype pattern , there should not be more than one object.
In prototyping, there are two type of cloning. A deep copy and shadow copy.
A deep copy refers to cloning a class contains many dependent member classes.
When we deep copy, all will be copped. Whether shadow copy refers to copping it self only.
Principles :
- Prototype instance will be used to specify instances.
- Copying this prototype object to create new objects.
UML :
I have mentioned an optional factory manager
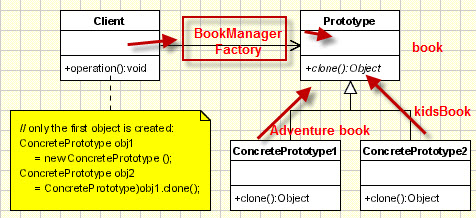
How to implement ?
Lets think about implementation, how can we make that. As we know we need
- A prototype that declares it self for cloning. Usually a connectable interface is the best way to do that. This connectable interface allows us to make it clone programmatically.
- Prototype implementing objects.
- Client who actually creates objects by asking prototype to clone it self.
We may use a prototype manager to keep tracks of of prototypes . It is like as factory that manages the prototypes.
Depending on the situation we may or may not use this.
In the example , I will use to have understand the facility to have a factory prototype. Lets see more details in code.
Example :
Let’s talk about a small scenario to implement factory.
Suppose we in a Book Fair. We do not know about book. As, client do not know any particular book, it will create a book and clone the book. And client will clone that with abstraction. That means we need
- Client who make a type of book( let consider adventure book and detective book here). In the example, it contains main method. I will add hash code value of the objects to keep understand objects are created and having different location(cloned).
- BookManagerFactory(I have used this factory in the example) that used to take the responsibility to to do cloning without knowing what is he cloning(fully abstract/interface calling)
- An abstract class/interface BookPrototype which is closeable. I have use Interface.
- Two subclass implementing that interface. I have applied Adventure books and kids book.
Main Goal :
Our client will call adventure book and clone it. We will see the two objects(original and cloned) have different addresses.
So, the prototype interface IBookPrototype
public interface IBookPrototype extends Cloneable{
public IBookPrototype makeAClone();
}
And Prototype implementing sub classes.
public class AdventureBook implements IBookPrototype{
public AdventureBook(){
System.out.println("An adventure book is bought");
}
public IBookPrototype makeAClone() {
AdventureBook aBook=null;
try {
aBook = (AdventureBook)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("An adventure book is cloned");
return aBook;
}
}
public class KidsBook implements IBookPrototype{
public KidsBook(){
System.out.println("A Kids book is bought");
}
public IBookPrototype makeAClone() {
KidsBook aBook=null;
try {
aBook = (KidsBook)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("A Kids book is cloned");
return aBook;
}
}
And now, the factory. It actually do now know about specific sub class.
public class BookManagerFactory {
public IBookPrototype getClone(IBookPrototype abook) {
return abook.makeAClone();
}
}
So, from client(contains main class) we will clone object via factory and we will print hash code to prove that these are actually cloned.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookManagerFactory bookCloner = new BookManagerFactory();
IBookPrototype aCloneBook = null;
IBookPrototype aBook = new AdventureBook();
aCloneBook=(AdventureBook)bookCloner.getClone(aBook);
System.out.println("The hash code for original Adventure book = "+System.identityHashCode(aBook));
System.out.println("The hash code for cloned Adventure book = "+System.identityHashCode(aCloneBook));
aBook = new KidsBook();
aCloneBook=(KidsBook)bookCloner.getClone(aBook);
System.out.println("The hash code for original kid book = "+System.identityHashCode(aBook));
System.out.println("The hash code for cloned kid book = "+System.identityHashCode(aCloneBook));
}
}
Java Example :
- Extra factory method applied, you may use avoid it and directly call prototype.
- I have added some extra console printing to understand the steps properly.
C# Example:
- Cloning method name is changed
- Hash code method is changed
- Some methods are renamed as dot net works differently.
Usages :
- When we need to create object defined in run time.
- When we do not want to create factory hierarchy but still want to get the advantages.
- To keep the system independent for its object creation, composition as well as representation.
- When we need to create new object by cloning other object(not initiating).