In this article we are going to learn Visitor pattern.
- what is Visitor pattern?
- What are the basic principle?
- How we can implement that
- where we may use it.
I have use mainly Java with Eclipse and c# with VS2010.
What is visitor pattern?
In OO design, some time we need to add some extra function upon existing system(specifically objects) without changing the system.
Visitor pattern allow use to perform additional functionality over grouped or non grouped objects along with keep the functionality abstract from the operand(visitable) group.
In this pattern, there are mainly 2 type.
- Who will be visited are called Visitable/monitored objects
- Who will visitor/monitor visitable by adding new logic/functions to the visitable object.
This is the state Visitor pattern allows for one or more operation to be applied to a set of objects at run time, decoupling the operations from the object structure.
explain with examples:
Suppose, we are creating a reporting module for a group of customer. And the report must be detailed.
So, the customers will accepts the visitors and visitor(report generator) will access the information and process along with reporting logic and will be provided along with those visitors.
Another example, suppose a supermarket. Where the customers are visitable, and Cashiers are visitors.
When a customer check out, cashier visits, takes items from us and provide price memo and items in a bag. He also provide memo with tax calculation.
Previously we have seen similar pattern Decorator, but in here it is more generic. And, there is not dependency among each other and it makes added function logic(inside visitor) abstracted from the visitable objects.
We can also implement visitor classes using reflection to make it more dynamic.
Principles :
- Performs operations on the elements of an object structure(or may be a single object)
- Separate visitors from object structure.
- Visitor let us defines new operation without changing the operand class.
UML:
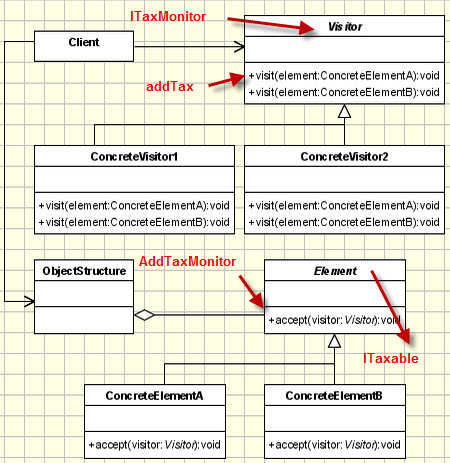
How to implement?
Generally, we see the whole system is based on 2 abstract class/interface(i have used interface). One is visitor and another is visitable.
Visitable defines the classes which will be visited. And, there should be at least one operation(method) in the visitable interface that will allow each implemented class will allow a visitor(the interface).
That means , visitable must have at least a method that allows visitors to see it monitor(visit) it self.
And, the Visitor interface. It will have the one or more functions that will be added one or more type of visitable objects. We have to specify the class to visit here because, each type of class may implement different added functionality. (from my example below, the tax of fruit and the tax of drinks may be different).
The visitor function will be implemented in the class level.
- We need classes that implements visitable along with its basic visiting properties.
- we need classes that will add functions upon the visitable implemented classes(in the example , i have change the price property).
- we need a client, who will make the visitable and use visitors to change the property(added functions) of the visitable objects.
Example:
Let’s think about a tax domain. There are different kind of tax applied for different kind of product. Les assume we have three kinds of products
- Chocolate
- Soft Drinks
- Fruits
And, as for govt rules, we have 3 kinds of taxes.
- Sales Tax(aka VAT) which is 1.5% for all items
- Source Tax(let assume a kind) which is 1% for Soft Drinks only.
- State Added Tax(additional tax specified by separate state of a country) which is 0.5% and it is for Chocolate and Soft Drinks.
Initially we will discuses code for only Sales Tax , you may find other implementations in code.
We have to implement visitor in a way so that any time if we need to add another kind of tax, we need minimal changes. Now, we have
- Products , which are taxable.
- Tax Inspectors will monitor the products.
Now, let make it generic way to apply visitor pattern. There will be interface for all products.
We need to apply interface for visitors in such way so that any time we can add more visitors.(in other words we can add more tax monitors, that is why I will explain one tax monitor and other monitors example are in the code, I will explain principle of adding. So that visitor pattern is explained.
And, we will have Client(contain main program) who will buy a product and automatically associated tax will be added.
So, lets start with visitable Interface ITaxable.
//The Visitable interface
public interface ITaxable {
public double addTaxMonitor(ITaxMonitor taxMonitor);
}
So, we see, a taxable product accept a monitor (or tax inspector) and it will return own price + price added by the monitor. And , interface for Visitors
//The visitor interface
public interface ITaxMonitor {
public double addTax(Chocolate aChocolate);
public double addTax(SoftDrink aDrink);
public double addTax(Fruit aFruit);
}
We see, it takes there products and return after adding taxes. So, lets implement ITaxable in products.
public class SoftDrink implements ITaxable{
private double price;
public SoftDrink(double aPRice){
price=aPRice;
}public double getPrice(){
return price;
}public double addTaxMonitor(ITaxMonitor taxMonitor) {
return taxMonitor.addTax(this);
}
}
public class Chocolate implements ITaxable{
private double price;
public Chocolate(double aPRice){
price=aPRice;
}
public double getPrice(){
return price;
}public double addTaxMonitor(ITaxMonitor taxMonitor) {
return taxMonitor.addTax(this);
}
}
public class Fruit implements ITaxable{
private double price;
public Fruit(double aPRice){
price=aPRice;
}public double getPrice(){
return price;
}
public double addTaxMonitor(ITaxMonitor taxMonitor) {
return taxMonitor.addTax(this);
}
}
If we see the addTaxMonitor, it will get a tax monitor(any type) and add the extra value by put it self in side the monitor to get the tax added price amount.Now, lets add client than contains main method and calls visitors as well as visitable classes.
public class Client {
public static DecimalFormat dt = new DecimalFormat("#.##");
public static void main(String[] args) {
SalesTaxMonitor vatMonitor = new SalesTaxMonitor();
Chocolate chocolate = new Chocolate(20);// price 20
SoftDrink drinks = new SoftDrink(40);// price 40
Fruit apple = new Fruit(15);// price 15
System.out.println("The VAT summary");
System.out.println(dt.format(chocolate.addTaxMonitor(vatMonitor)));
System.out.println(dt.format(drinks.addTaxMonitor(vatMonitor)));
System.out.println(dt.format(apple.addTaxMonitor(vatMonitor)));
}
}
For this example, I have added only price in a product to keep it simple.
We can add custom objects, but we have to be careful that the object which property we will change, we have keep that all over visitors and visitable interfaces.
Java Example :
- I have used public static DecimalFormat dt = new DecimalFormat(“#.##”); for getting good formatted decimal value only.
- Extra two tax monitor are added but not used.
C# Example:
- I have declared price as property.
- Some method are change as dot net works little differently.
Sources
Uses :
- It is used when similar operation needs to done on different types grouped objects .
- When object structure is non changeable but we need to add new operations over the objects.
- When we need to perform many non related operations on grouped (non grouped) objects.